Introduction
Welcome to Sibyl—the Collective Intelligence Runtime that transforms your AI agents from brilliant amnesiacs into knowledge-building collaborators.
What You'll Learn
This guide teaches you how to:
- Work with AI agents — The human guide to agent collaboration
- Set up your prompts — Configure CLAUDE.md for effective workflows
- Use skills and hooks — Automatic context injection
- Build a conventions repo — Centralize team patterns
- Manage knowledge — Through the web UI and CLI
- Orchestrate agents — Spawn autonomous agents with the harness
- Coordinate teams — Multi-agent patterns with shared memory
The Philosophy
Sibyl is built on a simple insight: AI agents are only as good as the context they have.
Most AI coding assistants start every session from scratch. They can't remember the OAuth gotcha you figured out yesterday. They don't know about the pattern that finally made your tests pass. They're brilliant, but amnesiac.
Sibyl fixes this by providing:
- Persistent Memory: Knowledge stored in a graph database survives forever
- Semantic Search: Find relevant patterns by meaning, not keywords
- Automatic Context: Hooks inject knowledge without manual prompting
- Structured Workflows: Skills teach agents the Research → Do → Reflect cycle
The Architecture
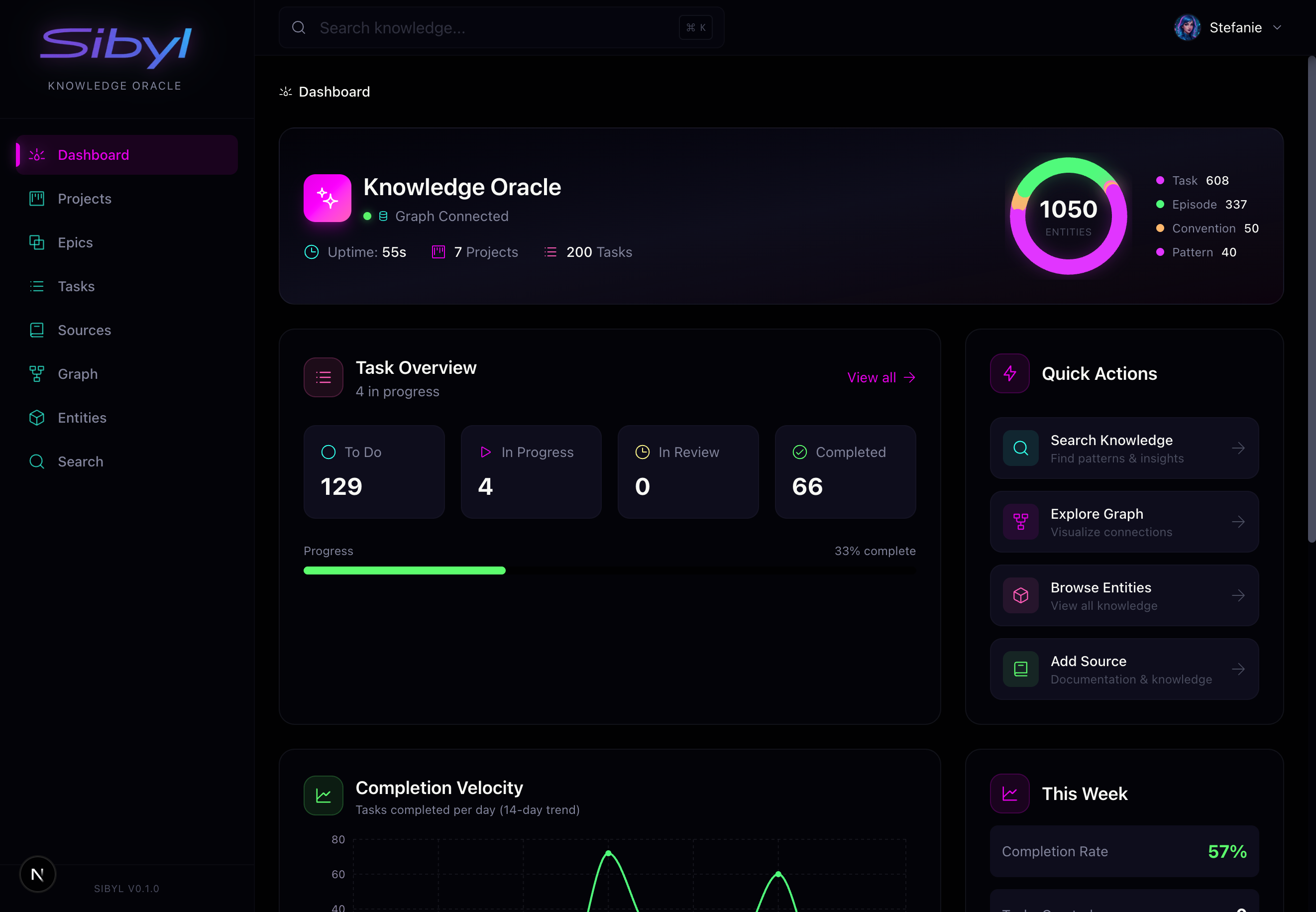
Sibyl consists of three main components:
1. Skills (For Agents)
Skills are documents that teach your AI agents how to work with Sibyl. When you invoke /sibyl in Claude Code, the agent receives:
- Command reference for all CLI operations
- Workflow patterns (when to search, when to capture)
- Best practices for knowledge quality
Agents don't need to figure out HOW to use Sibyl—skills teach them.
2. Hooks (Automatic Context)
Hooks are the magic that makes Sibyl invisible. They run automatically:
- SessionStart: Loads your active tasks when you begin a session
- UserPromptSubmit: Searches for relevant knowledge on every prompt
Your agent doesn't need to remember to search—relevant patterns appear automatically in their context.
3. Web UI (For Humans)
The web interface gives you visibility and control:
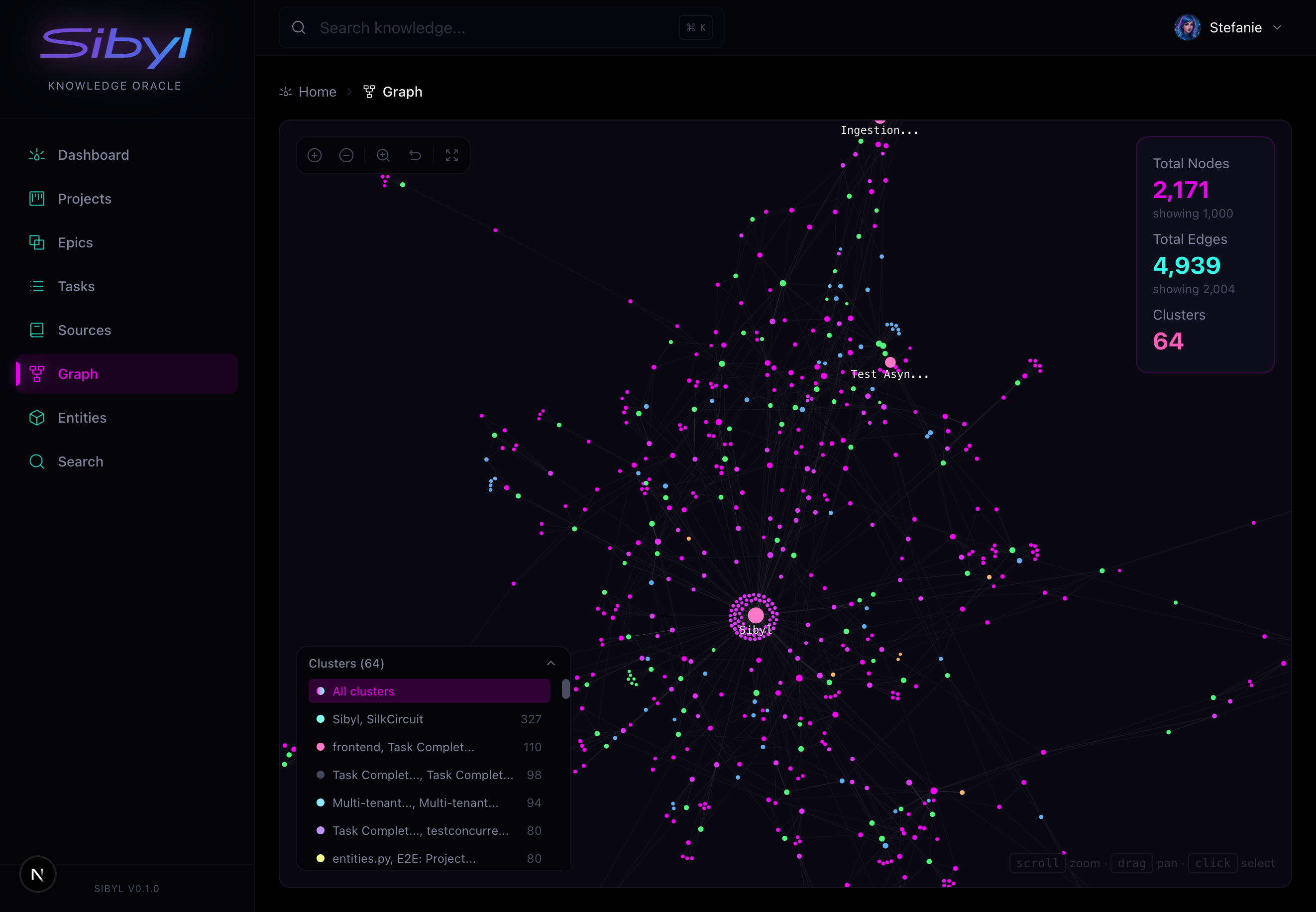
Graph Explorer: Visualize connections between entities, patterns, and learnings. See how knowledge clusters and relates.
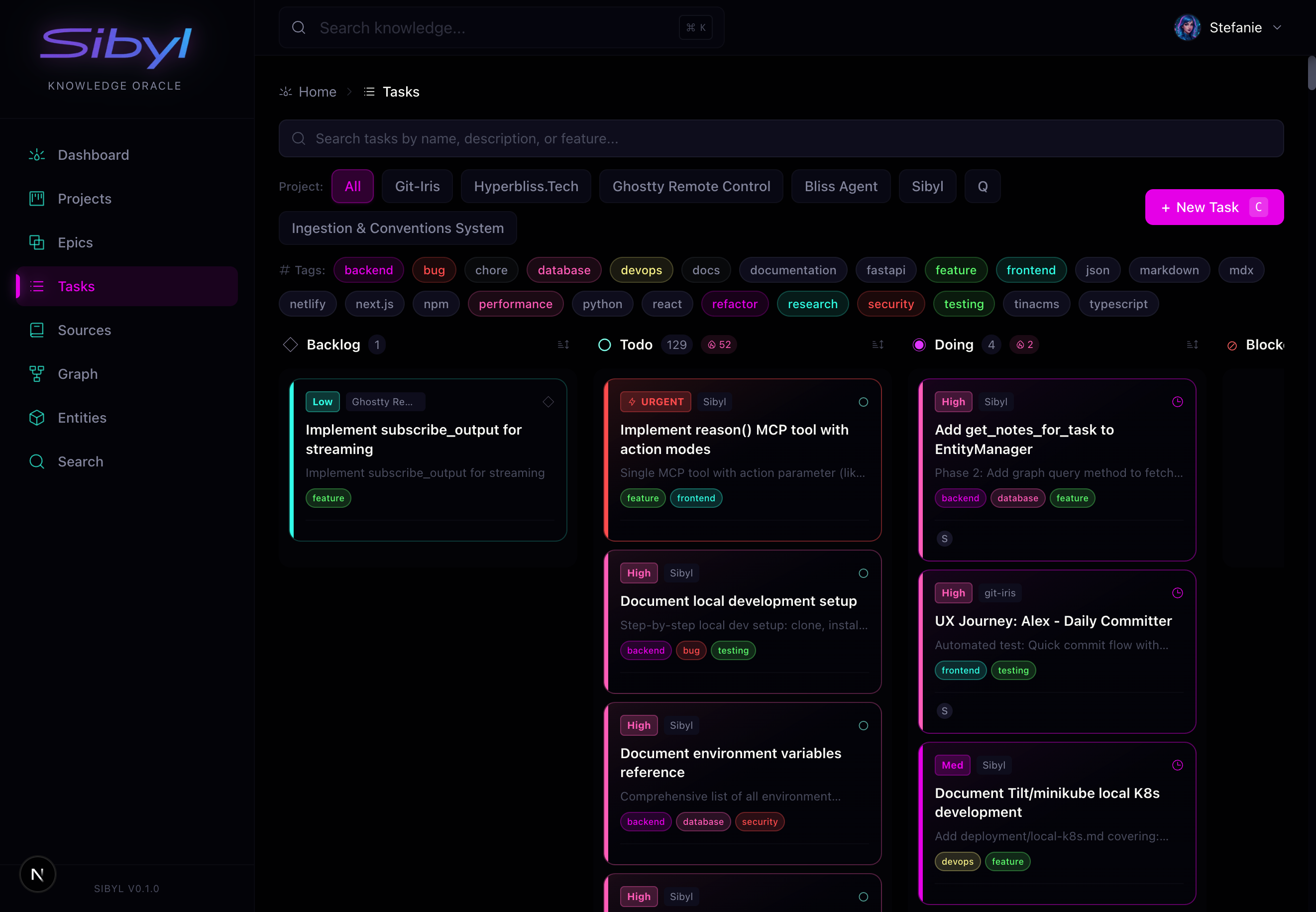
Task Management: Track work across projects with full lifecycle support. Filter by status, priority, assignee, and more.
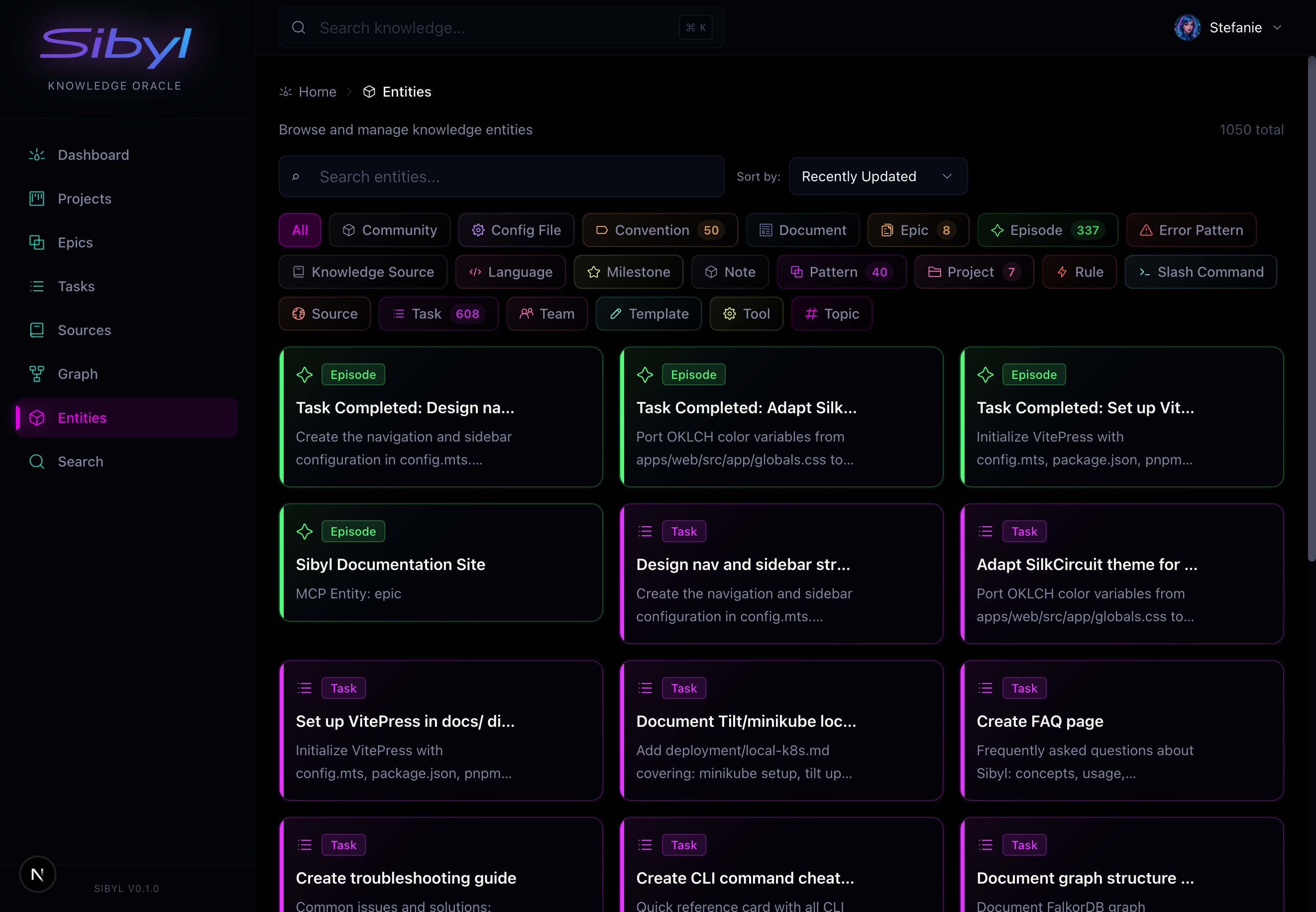
Entity Browser: Browse all knowledge types—patterns, episodes, conventions, rules. Search and filter to find what you need.
Semantic Search: Find knowledge by meaning across all entity types, documentation, and code.
The Workflow
Every effective Sibyl workflow follows the same cycle:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ RESEARCH │
│ Before implementing anything, search for existing │
│ patterns. Your past self (or other agents) may have │
│ already solved this problem. │
│ │
│ sibyl search "what you're about to implement" │
└─────────────────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ DO │
│ Work on your task with the context you found. │
│ Track progress with task lifecycle commands. │
│ │
│ sibyl task start task_xyz │
└─────────────────────────┬───────────────────────────────┘
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ REFLECT │
│ When you finish, capture what you learned. │
│ Future agents will thank you. │
│ │
│ sibyl task complete task_xyz --learnings "..." │
│ sibyl add "Pattern Title" "What you discovered..." │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘What to Capture
Not everything belongs in the knowledge graph. Focus on:
Always Capture
- Non-obvious solutions: If it took time to figure out, save it
- Gotchas and quirks: Configuration issues, platform differences
- Architectural decisions: Why you chose approach A over B
- Error patterns: Problems and their root causes
Consider Capturing
- Useful patterns: Reusable code structures
- Performance findings: What made things faster
- Integration approaches: How to connect systems
Skip
- Trivial info: Things obvious from documentation
- Temporary hacks: Quick fixes that should be replaced
- Well-documented basics: Standard library usage
Quality Bar
The knowledge graph gets smarter with every entry—but only if entries are high quality.
Bad entry:
"Fixed the auth bug"
Good entry:
"JWT refresh tokens fail silently when Redis TTL expires. Root cause: token service doesn't handle WRONGTYPE error. Fix: Add try/except with token regeneration fallback. Prevention: Always handle Redis type mismatches in token renewal logic."
The good entry includes:
- What happened
- Root cause
- How to fix it
- How to prevent it
CLI vs MCP vs Web UI
Sibyl offers three interfaces, each suited to different users:
| Interface | Best For | Token Usage |
|---|---|---|
| CLI | Agents doing scripted work | Low—text output only |
| MCP | Direct tool invocation | Higher—full JSON schemas |
| Web UI | Humans managing projects | N/A—visual interface |
For AI agents, prefer the CLI for routine operations. It's more expressive, enables scripting, and uses fewer tokens than MCP tool calls.
Distributed Execution
Sibyl includes a sandbox system for distributed task execution via runner daemons. Runners provide isolated, ephemeral environments where AI agents can execute tasks safely — from local process-level isolation for development up to Kubernetes pod-level isolation for production.
Key capabilities:
- Isolated environments — Each task runs in its own sandboxed context
- BYOD runners — Bring your own compute; runners self-register with capabilities
- Automatic routing — Tasks are dispatched to the best available runner based on availability, capability match, and warm worktree proximity
- Multiple isolation tiers — Local, Docker, Kubernetes, and vCluster
For the full technical design, see Sandbox Architecture.
Next Steps
Getting Started
- Installation — Get Sibyl running locally
- Quick Start — Create your first knowledge entries
Working with Agents
- The Human Guide — How YOU work with AI agents
- Setting Up Prompts — Configure your CLAUDE.md
- Skills & Hooks — Automatic context injection
- Conventions Repository — Centralize team patterns
Core Concepts
- Knowledge Graph — Understand the data model
- Task Management — Track work across sessions
- Agent Harness — Autonomous agent orchestration
- Sources — Ingest external documentation
